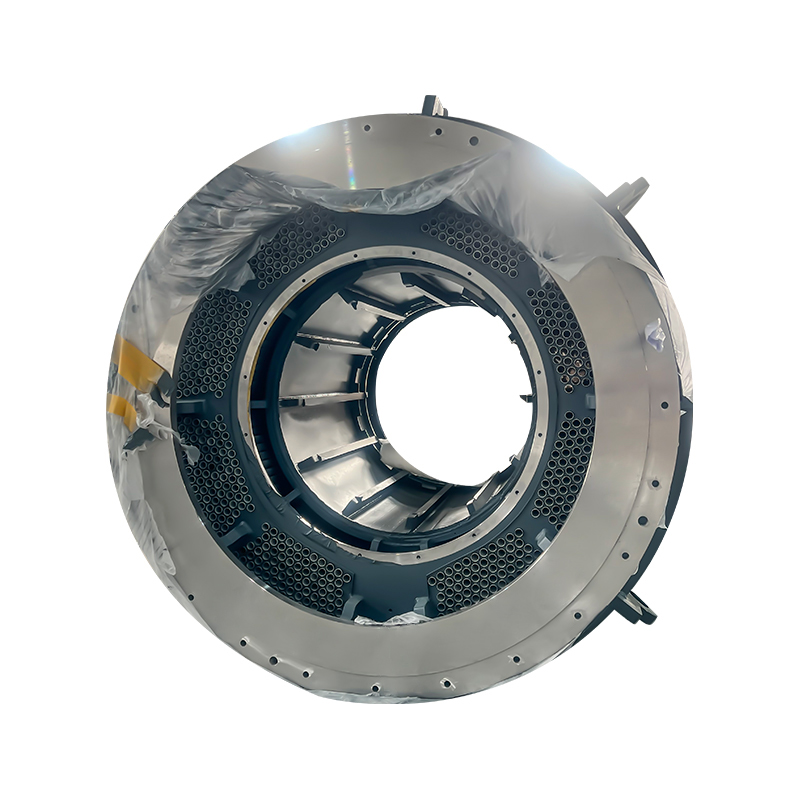
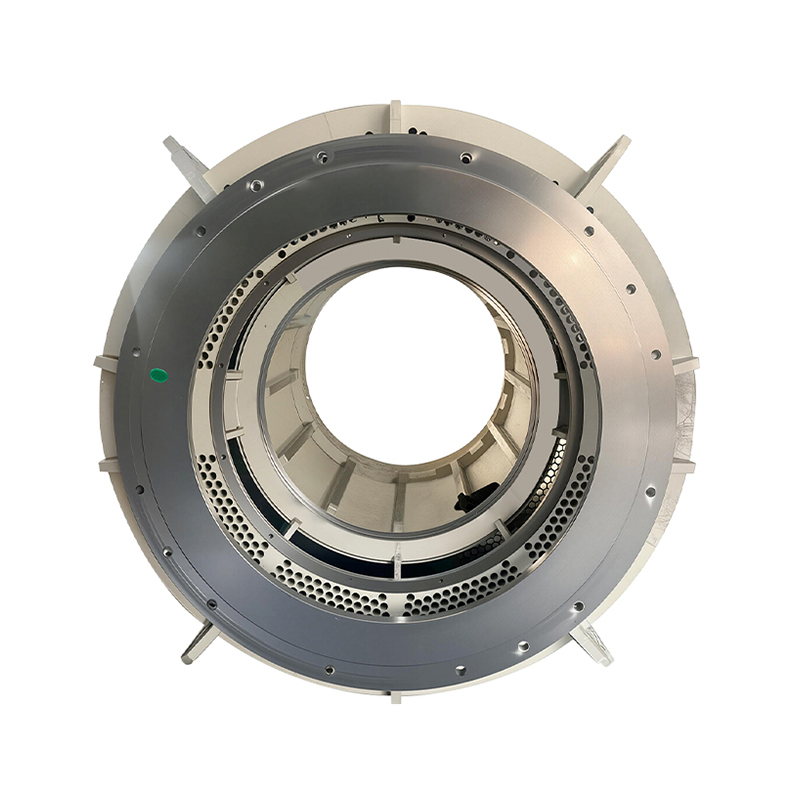
Core Structural Features
Vertical Cylindrical Architecture: The main body features a cylindrical casing arranged in a vertical configuration. The base is fixed to the floor with an annular flange and anchor bolts, while the top supports the motor/equipment body. This layout reduces the horizontal footprint by more than 50% compared to square bases.
Industrial-Grade Materials and Protection: The casing is made from Q235B/Q345B industrial steel plates (large models are welded together). The surface undergoes rust removal and spray painting/plastic coating to adapt to industrial environments with dust, oil, moisture, etc. It comes with an IP54 protection rating as standard, with customized versions available up to IP65.
Internal Reinforced Support Ribs: The interior features 6-12 sets of radial support ribs evenly distributed, connecting the casing to the central positioning sleeve. This design enhances rigidity and heat dissipation, ensuring concentricity of the shaft system.
Modular Adaptation Structure: The top is equipped with a standardized positioning stop, allowing for quick connection with various models of vertical motors. The base is fitted with adjustable shock-absorbing feet (rubber material), which accommodate uneven workshop floors and absorb vertical vibrations.
Key Advantages
1. Strong Adaptability to Industrial Space
The vertical layout can be embedded into production line mezzanines, adjacent to equipment columns, or other tight vertical spaces. It is particularly suitable for environments where equipment density is high, and horizontal space is limited (e.g., machining factories, chemical plants, and construction material production lines).
The cylindrical shape has no sharp corners, making it easier for workers to move around and arrange equipment. This reduces the risk of collisions and enhances space utilization in the workshop.
2. Stable Structure with Cost Control
The axis-symmetric cylindrical structure ensures uniform load distribution and outstanding resistance to industrial vibrations (such as those from machine tools or fan-induced vibrations). The operating noise is reduced by 8-10 dB compared to square bases.
With a simplified structure, there is no need for a complex cooling system (default natural heat dissipation; an optional external fan cooling kit is available). This design reduces manufacturing costs by 20-30% compared to marine versions, making it highly suitable for mass production.
3. Efficient and Convenient Installation and Maintenance
Vertical lifting positioning allows for quick setup, with the standardized base flange design enabling two workers to complete the installation within half a day, without the need for complex on-site machining.
The casing includes a reserved inspection window, and the internal support ribs do not obstruct core components, allowing for direct access to repair the motor base or shaft seals. This reduces maintenance downtime by 30%.
The adjustable anchor bolts support ±3° of horizontal fine-tuning, enabling rapid calibration of the shaft verticality, thus reducing installation and debugging difficulty.
4. Multifunctional Adaptation to Industrial Needs
Compatible with 50-1000kW small and medium-sized vertical motors, covering core industrial equipment such as vertical pumps, fans, mixing equipment, and conveyor motors.
Customizable casing diameter (300-1500mm) and casing height (500-2000mm) to meet the load-bearing and installation size requirements of different motor power ratings.
High-temperature models can be equipped with external heat-dissipating fins, improving natural heat dissipation efficiency by 25%, making them suitable for workshops with temperatures above 40°C.

 en
en
 русский
русский Deutsch
Deutsch